Trading Data Model API
The Trading Data Model API document describes Order Entry API used by Execution Server, Quote Flow and other Deltix products. Market Data model is described in a separate document.
Concept
Deltix Trading API is influenced by the FIX Protocol and native APIs of various trading systems that Deltix has previously worked with. It is designed to provide a high-level normalized format suitable to interact with 99% of trading venues.
The Primary API language is Java. Currently, Deltix provides only Java and C# binding of the API.
Requests And Events
Depending on their direction messages are divided into trading Requests and trading Events. Each request results in one or in several response events.
The Current version supports four types of trading requests:
OrderNewRequest - places a new order on the market
OrderCancelRequest - cancels a previously placed order
OrderReplaceRequest - modifies a previously placed order
OrderStatusRequest - request information about the current order status
For users familiar with FIX protocol, these requests correspond to the NewOrderSingle(D), OrderCancelRequest(F), OrderReplaceRequest(G), and OrderStatusRequest(H) FIX messages.
When it comes to trading events, the system currently supports the following types:
OrderPendingNewEvent - the trading venue that has received the order, but it is not on the market yet
OrderNewEvent - the order is working in the market of the trading venue destination
OrderRejectEvent - the trading venue or market rejected the order
OrderPendingCancelEvent - trading venue is processing order cancellation request
OrderCancelEvent - the trading venue or the market rejected the order
OrderCancelRejectEvent - the trading venue cannot cancel the order
OrderTradeReportEvent - reports a trade - the order is filled (completely or partially)
OrderPendingReplaceEvent - the trading venue received an order modification request
OrderReplaceEvent - the trading venue modified an order on the market
OrderReplaceRejectEvent - the trading venue rejected an order modification request
OrderStatusEvent - trading venue reports the current order status (filled amount, etc.)
OrderRestateEvent - the trading venue changed some order parameter (e.g. stop order is triggered)
Users familiar with the FIX protocol will recognize that most of these events represent different types of Execution Report message:
| API Event | FIX Protocol |
|---|---|
| OrderPendingNewEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=A Pending New |
| OrderNewEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=0 New |
| OrderRejectEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=8 Reject |
| OrderPendingCancelEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=6 Cancel |
| OrderCancelEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=4 Cancel or =C Expired |
| OrderCancelRejectedEvent | OrderCancelReject(9) with CxlRejResponseTo(434)=1 Cancel Request |
| OrderTradeReportEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=F Trade |
| OrderTradeCorrectEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=G Trade Correct |
| OrderTradeCancelEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=H Trade Cancel |
| OrderPendingReplaceEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=E Pending Replace |
| OrderReplaceEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=5 Replace |
| OrderReplaceRejectEvent | OrderCancelReject(9) with CxlRejResponseTo(434)=2 Replace Request |
| OrderStatusEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=I Status |
| OrderRestateEvent | ExecutionReport(8) with ExecType(150)=D Restated |
Order Status versus Order Event type
As you already know, the Deltix trading model is inspired by FIX Protocol. This section is almost a direct quote from FIX Protocol Volume 4: Orders and Execution, section that describes FIX Execution Reports.
Order events communicate the following:
- Confirm the receipt of an order
- Confirm changes to an existing order (i.e. accept cancel and replace requests)
- Relay order status information
- Relay fill information on working orders
- Reject orders
In each case a specialized event is used to convey what happened to the order (or the purpose of the event), while attribute orderStatus available in each event conveys the current state of the order (as understood by execution venue). If an order simultaneously exists in more than one order state, the value with the highest precedence is the value that is reported in the OrdStatus field. The order statuses are as follows (in highest to lowest precedence):
| Precedence | Order Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | Pending Cancel | Order with an Order Cancel Request pending, used to confirm receipt of an Order Cancel Request. DOES NOT INDICATE THAT THE ORDER HAS BEEN CANCELED. |
| 6 | Pending Replace | Order with an Order Cancel/Replace Request pending, used to confirm receipt of an Order Cancel/Replace Request. DOES NOT INDICATE THAT THE ORDER HAS BEEN REPLACED. |
| 5 | Filled | Order completely filled, no remaining quantity. |
| 4 | Suspended | Order has been placed in suspended state at the request of the client. |
| 3 | Canceled | Cancelled order with or without executions. |
| 3 | Expired | Order has been canceled in the broker's system due to time in force instructions. |
| 2 | Partially Filled | Outstanding order with executions and remaining quantity |
| 1 | New | Outstanding order with no executions. |
| 1 | Rejected | Order has been rejected by sell-side (broker, exchange, ECN). NOTE: An order can be rejected after order acknowledgment, i.e. an order can pass from New to Rejected status. |
| 1 | Pending New | Order has been received by sell-side’s (broker, exchange, ECN) system but not yet accepted for execution. An execution message with this status will only be sent in response to a Status Request message. |
For example, algorithmic order may receive a fill while pending cancellation. In this case OrderTradeReport Event will be used to convey the filled amount and price. However, orderStatus in this event will be set to "Pending Cancel".
Another example| Imagine you have an IOC (Immediate-or-Cancel) order. In some cases, partial fill and cancellation for such orders may be reported using a single OrderTradeReportEvent with orderStatus set to "Cancelled".
Source and Destination
Each message has a source and a destination. Requests and Events that come in response usually reverse their source and destination. In other words, the event's destination identifies the request source and vice versa.
The Source is required while the Destination is optional. When a destination is unspecified, the system may route messages according to some custom rules.
In the Trading API, both the Source and the Destination are represented by INT64.
For example, the Execution Server uses ALPHANUMERIC(10) encoding to convert human-readable sources and destinations into their INT64 identifiers (there is a separate section below that describes this encoding in detail).
Identity
The API follows the FIX protocol when it comes to identifying orders and requests.
Order ID
Each API client or algorithm provides ID with each order. This textual identifier is unique only in scope of a specific order source (identified by Source ID).
Each time the order is modified, the client provides a new order ID and must specify the original order ID. Once the change is approved, the working order will be identified by the ID of the replacement order request. In case of the replace-reject, the order keeps its original identity. Users familiar with the FIX protocol will recognize this approach.
For the convenience of handling the large chain of cancellation replaces requests, the API supports Correlation Order ID. This optional attribute matches the ID of the first order in the replacement chain. Concept of Correlation ID can also be found in trading APIs like CME iLink.
External Order Id
Trading Venues may assign their identifiers to the orders, represented as an \"external order ID\". These identifiers are unique only in the scope of each trading venue (identified by Destination ID and Exchange).
An external order ID is typically reported with order events and may or may not change each time the order is modified using CancelReplaceRequest.
Request ID
To distinguish repeated attempts to cancel the same order, each CancelRequest is identified by a Request ID. This required identifier is subsequently reported in the ACK / NACK events OrderCancelEvent and OrderCancelRejectEvent cancel events.
Correlation Order ID
When order undergoes Cancel Replace workflow each OrderReplaceRequest uses separate unique order ID and identifies which [predecessor] order request it replaces using Original Order ID attribute. For example, if order was replaced twice, cancel replace chain will have three order identifies - original order and two replacement requests.
For any Cancel Replace chain of messages optional attribute Correlation Order ID identifies the very first order in the chain. This attribute can be provided by API user. OMS automatically populate this attribute for downstream messages.
Required and Optional attributes
Each message in the API has a set of required and optional fields. For example, in each order event field, the Order ID is required, while the External Order ID field is optional.
Refer to sources/javadoc to get information on each field. Typically, optional fields have additional logical methods that check whether a field is defined or not. For example, OrderEvent.hasExternalOrderId() method. The Ember Java binding of this API also uses @Required or @Optional annotations when defining field getters and setters.
Field Enrichment
When a trading message passes through the Deltix OMS system on its way to the destination, it undergoes the enrichment step. OMS attempt to define all optional attributes from the context. For example, the OMS can define instrument type based on the order symbol. For messages that affect a previously known order, OMS can copy the missing fields from the last known order state. That is, the OMS can derive order symbol and side (BUY or SELL) for CancelRequest from the symbol and side specified during the order submission. Some trading venues require order side, symbol, etc. field for each cancellation request.
Quantities
In accordance with FIX protocol when you modify order you need to specify total desired order quantity.
The following table illustrates various quantity-related attributes on requests and events. Original order quantity is 5 which is subsequently increased to 10. During this time order receives partial fills.
| Message | Quantity | Trade Quantity | Cumulative Quantity | Remaining Quantity | Order State |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OrderNewRequest | 5 | UNACKNOWLEDGED | |||
| OrderNewEvent (ACK) | 5 | 0 | 5 | NEW | |
| OrderTradeReportEvent | 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | PARTIALLY FILLED |
| OrderTradeReportEvent | 5 | 1 | 3 | 2 | PARTIALLY FILLED |
| OrderReplaceRequest | 10 | PARTIALLY FILLED | |||
| OrderReplaceEvent (ACK) | 10 | 3 | 7 | PARTIALLY FILLED | |
| OrderTradeReportEvent | 10 | 7 | 10 | 0 | COMPLETELY FILLED |
Custom Attributes
The FIX Protocol specifies many more fields than are represented in the Deltix Trading API. While Deltix has attempted to represent the most common fields, in remaining cases one can rely on custom attributes.
Each trading message can carry a list of custom attributes. Each attribute is identified by numeric key and stores the text value.
Mutable and Immutable messages
For each message in the Trading API there is usually an immutable interface that is presented to message consumers, and a mutable message [interface] that is available to message producers.
For example, OrderCancelEvent and MutableOrderCancelEvent. Similarly, in the TimeBase API, these messages are called OrderCancelEventInfo and OrderCancelEventInterface.
Supported codecs
TimeBase - Trading Messages can be stored and loaded from TimeBase.
Binary - Deltix Execution Server includes a set of high-performance codecs to work with in-memory buffers or communication frameworks such as Aeron
JSON - Messages can be converted back and forth into JSON
FIX - FIX Server components include codecs into FIX 4.4
Special Types
Decimal
Unfortunately, in the Java language, there is no data type for accurate money representation. Built-in type \'double\' introduces rounding errors, while BigDecimal is slow and immutable (requires frequent memory allocations).
Deltix uses Decimal64 IEEE 754 format to represent prices and sizes using INT64 (Java \'long\') data type.
You can find more information about Decimal64 on GitHub: https://github.com/epam/DFP.
Things to remember:
- Use @Decimal annotation to mark fields, parameters, methods that pass Decimal64 values using INT64 data type.
- Use com.epam.deltix.decimal.Decimal64Util for conversions to various data types and most frequently used operations.
Here is an example of how decimal expressions may look like in your code:
import com.epam.deltix.dfp.Decimal64Util.*;
@Decimal final long totalValue = add(order.getTotalExecutedValue(), multiply(event.getTradePrice(), event.getTradeQuantity()));
With a little practice, these this prefix math operations are easy to follow.
Timestamp
All timestamps are stored as INT64 (Java \'long\') data type for more effectiveness. Numeric value stores number of milliseconds since midnight on January 1st, 1970 (Linux epoch time).
Use @Timestamp annotation to mark fields, parameters, methods that represent timestamps values using INT64 data type.
This timestamp format corresponds to java.util.Date and java.util.Calendar millisecond time.
Alphanumeric
In many cases, short textual identifiers, such as exchange codes, or component names (used as Source or Destination IDs), can be efficiently stored in the single INT64 data type. In this case, Deltix uses ALPHANUMERIC(10) TimeBase encoding.
ALPHANUMERIC(10) text values must not exceed 10 characters. Valid characters are upper case letters, and digits, and punctuation chars (ASCII range 0x20..0x5F).
For example text "COINBASE" is encoded as 0x88EFA6E8A1CE5000 and represented inside INT64 as shown below:

Use @Alphanumeric Java annotation to mark fields, parameters, methods that transmit ALPHANUMERIC-encoded text values using INT64 data type.
The following Java algorithm implements this encoding:
public static long parse(final CharSequence text) {
if (text == null)
return TypeConstants.ALPHANUMERIC_NULL;
int length = text.length();
if (length > 10)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Text \"" + text + "\" exceeds max length of alphanumeric text");
long value = (long) length << 60L;
for (int i = 0, shift = 54; i < length; i++, shift -= 6) {
final char c = text.charAt(i);
if (c < 0x20 | c > 0x5F) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Text \"" + text + "\" contains non-alphanumeric char at " + i);
}
value |= (c - 0x20L) << shift;
}
return value;
}
Samples
Here we include several fragments to show you how the actual Order Entry API looks like:
Order Submission
The following sample fills Order New Request for new order submission:
MutableOrderNewRequest request = new MutableOrderNewRequest();
request.setOrderId(idGenerator.next());
request.setSide(side);
request.setQuantity(FP.fromLong(size));
request.setSymbol(symbol);
request.setLimitPrice(FP.fromDouble(price));
request.setTimeInForce(TimeInForce.DAY);
request.setOrderType(OrderType.LIMIT);
request.setDestinationId(getServiceByName("marketfactory"));
request.setExchangeId(ExchangeCodec.codeToLong("HOTSPOT"));
request.setSourceId(CLIENT_SOURCE_ID); // Identify order source
request.setTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
Order Fill Event
The following sample reports fill event:
tradeEvent.setSourceId(MARKET_FACTORY_SOURCE_ID);
tradeEvent.setSymbol(symbol);
tradeEvent.setTradeQuantity(tradeQuantity);
tradeEvent.setTradePrice(tradePrice);
tradeEvent.setDestinationId(orderEntry.getSourceId());
tradeEvent.setOrderId(orderEntry.getOrderId());
tradeEvent.setExternalOrderId(orderEntry.getExternalOrderId());
tradeEvent.setSide(orderEntry.getSide());
tradeEvent.setEventId(tradeId);
tradeEvent.setCumulativeQuantity(orderEntry.getCumulativeQuantity());
tradeEvent.setAveragePrice(orderEntry.getAveragePrice());
tradeEvent.setRemainingQuantity(orderEntry.getRemainingQuantity());
tradeEvent.setAggressorSide(AggressorIndicator.ORDER_INITIATOR_IS_AGGRESSOR);
tradeEvent.setTimestamp(clock.time());
UML Diagram
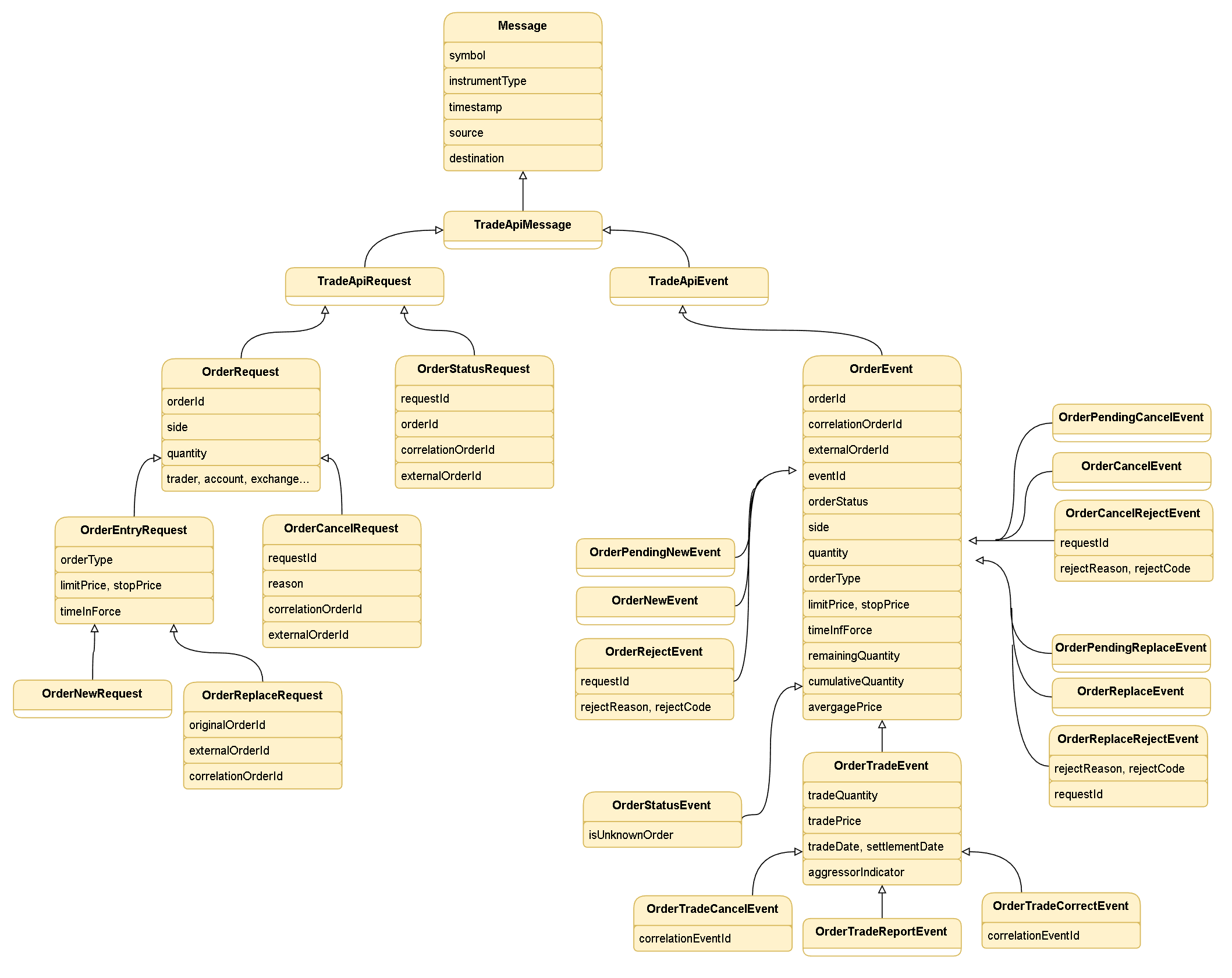
Mapping to FIX protocol
Trading Data Model used by Deltix is heavily influenced by messages of FIX Protocol. Deltix selected the most used subset of FIX tags and mapped them as "first class" attributes. Not so frequently used tags can be specified using custom message attributes. This section describes mapping of standard message attributes to FIX.
Standard attributes
| FIX Tag | Deltix API | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MsgType(35) | Mapped to a specific class, for example OrderNewSingle(35=D) is mapped to OrderNewRequest. | |
| ClOrdId(11) | Mapped to a pair {SourceId,OrderId} | See Order Id section |
| OrigClOrdId(41) | Mapped to a pair {SourceId, OriginalOrderId} | |
| Account(1) | Account | |
| Price(44) | LimitPrice | |
| StopPx(99) | StopPrice | |
| PegDifference(211) | PegDifference | Depends on trading connector |
| QuoteId(117) | QuoteID | Identifies quote for previously quoted order |
| MinQty(110) | MinQuantity | Depends on trading connector |
| MaxFloor(111) | DisplayQuantity | Depends on trading connector |
| TimeInForce(59) | TimeInForce | |
| ExpireDate(432) or ExpireTime(126) | ExpireTime | |
| Currency(15) | Currency | Depends on trading connector |
| Side(54) | Side | |
| OrderQty(38) | Quantity | Trading connectors may perform quantity translation (using size multiplier) |
| OrdType(40) | OrderType | |
| Clearing Account (440) | ClearingAccount | |
| SenderSubID(50) | TraderId | Depends on trading connector |
| ExDestination(100) | Exchange | Depends on trading connector |
| Symbol(55) | Symbol | Trading connectors may perform symbol translation |
| SecurityType(167) | InstrumentType | |
| TransactTime(60) | Timestamp | |
| ExBroker(76) | Destination | Depends on trading connector |
| Text(56) | UserData | Depends on trading connector |
| Commission(12) | Commission | On events only |
| LastPx(31) | TradePrice | On events only |
| LastShares(32) | TradeQuantity | On events only |
| TradeDate(75) | TradeDate | On events only |
| FutSettlDate(64) | SettlementDate | On events only |
| AggressorIndicator(1057) | AggressorSide | On events only |
| MultiLegReportingType(442) | MultiLegReportingType | On events only |
| OrdStatus(39) | OrderStatus | On events only |
| ExecType(150) and ExecTransType(20) | Mapped to event type (e.g. OrderTradeReportedEvent is 150=F) | On events only |
| ExecId(17) | EventId | On events only |
| CumQty(14) | CumulativeQuantity | On events only |
| AvgPx(6) | AveragePrice | On events only |
| LeavesQty(151) | RemainingQuantity | On events only |
| TransactTime(60) | OriginalTimestamp | On events only |
Custom Attributes
The following code example demonstrates use of custom order attributes.
import deltix.ember.util.CustomAttributeListBuilder;
private static void addCustomAttributes(MutableOrderNewRequest request) {
attributeListBuilder.clear();
// Repeated group
attributeListBuilder\
.addInteger(Tag.NoPartyIDs, 2)
.addText(Tag.PartyID, "AAA\")
.addInteger(Tag.PartyRole, PartyRole.CLIENT_ID)
.addText(Tag.PartyID, "BBB")
.addInteger(Tag.PartyRole, PartyRole.AGENT);
attributeListBuilder
.addTimestamp(7050, System.currentTimeMillis() + 1000);
request.setAttributes(attributeListBuilder.build());
}
Multi-legged contracts
Data model supports multi-legged securities (e.g. Calendar spreads on CME exchange).
Trading request should simply use multi-legged security symbol (for example, "ZFH20-ZFM20" is calendar spread on US Treasury Bond Future contracts). Optionally instrument type "MLEG" (MULTI_LEG_INSTRUMENT) can be supplied with each request.
When processing fills for multi-legged orders you should pay attention to MultiLegReportingType and Symbol attributes of events.
Example of a fill event for individual leg:
OrderTradeReport.setMultiLegReportingType(INDIVIDUAL_LEG_SECURITY);
OrderTradeReport.setSymbol("ZFH20") <-- identifies *leg* instrument
Example of fill even for multi-legged contract:
OrderTradeReport.setMultiLegReportingType(MULTI_LEG_SECURITY);
OrderTradeReport.setSymbol("ZFH20-ZFM20") <-- identifies *spread* instrument
Order Statuses
There following is a list of status codes supported by our product.
| Status | Final | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UNACKNOWLEDGED | N | Order has not been submitted yet (Same as OrderStatus.PendingSubmit in QuantOffice API). |
| ACKNOWLEDGED | N | Acknowledged by trading provider, waiting to become open (Also was known as \"ACKNOWLEDGED\"). |
| OPEN | N | Submitted but not yet executed (Also was known as \"OPEN\"). |
| OPEN_PARTIALLY_FILLED | N | Partially filled. |
| COMPLETELY_FILLED | Y | Completely filled. In case of cancel-replace chains this status means that cumulative executed quantity of entire chain reached requested size. |
| REJECTED | Y | Rejected |
| CANCELLED | Y | Cancelled |
| UNACKNOWLEGED | N | Deprecated version of UNACKNOWLEDGED - keeping for API compatibility |